Tuesday, February 04, 2014
liberals do everything wrong: the strict-father will always smash the cathedral
By
CNu
at
February 04, 2014
0
comments
![]()
Labels: Cathedral , ethology , killer-ape , the wattles
these humans....,
By
CNu
at
February 04, 2014
0
comments
![]()
Labels: neuromancy , What IT DO Shawty...
Monday, February 03, 2014
where is the proof in pseudo-science?
By
CNu
at
February 03, 2014
6
comments
![]()
Labels: culture of competence , What IT DO Shawty...
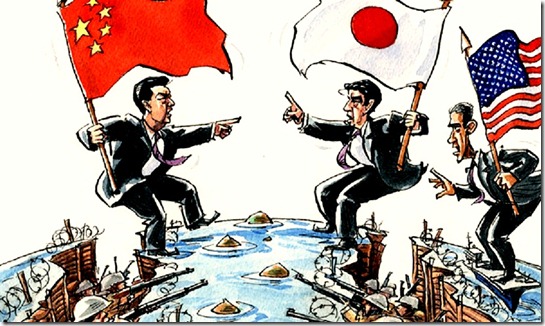
echo of past world war from davos...,
Disconcerting remarks that seem to have freaked out many who attended the events (two separate events at Davos - confab of the rich and the powerful in the world), but there is hardly a peep about them in Japan. I don't think either remarks were reported by the Japanese media.
First, about the incredible Chinese professional, from Business Insider's Henry Blodget, who was at a dinner at Davos where he heard the following (1/22/2014; emphasis is mine):
I went to one of those fancy private dinners last night in Davos, Switzerland.
Like most of the events here at the 2014 World Economic Forum, the dinner was conducted under what are known as "Chatham House Rules," which means that I can't tell you who was there.
I can tell you what was said, though. And one thing that was said rattled a lot of people at the table.
During the dinner, the hosts passed a microphone around the table and asked guests to speak briefly about something that they thought would interest the group.
One of the guests, an influential Chinese professional, talked about the simmering conflict between China and Japan over a group of tiny islands in the Pacific.
China and Japan, you may recall, each claim ownership of these islands, which are little more than a handful of uninhabited rocks between Japan and Taiwan. Recently, the Japan-China tension around the islands has increased, and has led many analysts, including Ian Bremmer of the Eurasia Group, to worry aloud about the potential for a military conflict.
The Chinese professional at dinner last night did not seem so much worried about a military conflict as convinced that one was inevitable. And not because of any strategic value of the islands themselves (they're basically worthless), but because China and Japan increasingly hate each other.
By
CNu
at
February 03, 2014
0
comments
![]()
Labels: WW-III
Sunday, February 02, 2014
Synarchism: The Root of Fascism and Fascist Root of __________________?
 |
| Synarchism - the fascist roots of the Wolfowitz cabal |
wikipedia | The most substantial early use of the word "synarchy" comes from the writings of Alexandre Saint-Yves d'Alveydre (1842–1909), who used the term in his book La France vraie to describe what he believed was the ideal form of government.[3] In reaction to the emergence of anarchist ideologies and movements, Saint-Yves elaborated a political formula which he believed would lead to a harmonious society. He defended social differentiation and hierarchy with collaboration between social classes, transcending conflict between social and economic groups: synarchy, as opposed to anarchy. Specifically, Saint-Yves envisioned a Federal Europe (as well as all the states it has integrated) with a corporatist government composed of three councils, one for academia, one for the judiciary, and one for commerce.
Rule by a secret elite Some conspiracy theorists use the word "synarchy" to describe a shadow government, a form of government where political power effectively rests with a secret elite, in contrast to an "oligarchy" where the elite is or could be known by the public.[5]
Occultism Some authors[who?] have claimed that Saint-Yves was a "theocratic occultist" who used "synarchy" to describe a form of government where political power effectively rests with secret societies or, more precisely, esoteric societies, which are composed of oracles. Furthermore he is supposed to have associated "synarchy" with the rule of "ascended masters" who lived in the subterranean caverns of Agartha and supposedly communicated with him telepathically.[6] However, other authors[who?] have described these claims about Saint-Yves as false and originating in occult conspiracy theories.[citation needed]
In Vichy France According to former OSS officer William Langer (Our Vichy Gamble, Alfred A Knopf, New York, 1947), there were French industrial and banking interests who "even before the war, had turned to Nazi Germany and had looked to Hitler as the savior of Europe from Communism. These people were as good fascists as any in Europe. Many of them had extensive and intimate business relations with German interests and were still dreaming of a new system of 'synarchy', which meant government of Europe on fascist principles by an international brotherhood of financiers and industrialists."
This theory allegedly originated with the discovery of a document called Pacte Synarchique following the death of Jean Coutrot, former member of Groupe X-Crise, on May 15, 1941. According to this document, a Mouvement Synarchique d'Empire had been founded in 1922, with the aim of abolishing parliamentarianism and replacing it with synarchy. This led to the belief that La Cagoule, a far-right organisation, was the armed branch of French synarchism, and that some important members of the Vichy Regime were synarchists. An investigation was in fact ordered by the Vichy government, leading to the Rapport Chavin[7] but no evidence for the existence of the Mouvement Synarchiste d'Empire was found. Most of the presumed synarchists were either associated with the Banque Worms or with Groupe X-Crise and were close to Admiral François Darlan, and this has led to the belief that synarchists had engineered the military defeat of France for the profit of Banque Worms.[8]
This belief system has been dismissed as a "work of a paranoid imagination which wove together the histories of three disparate groups of activists, creating a conspiracy among them where none existed".[9] In fact, some historians suspect that the Pacte Synarchique was a hoax created by some members of La Cagoule to weaken Darlan and his technocrats.[10]
Propaganda Due The Propaganda Due lodge (P2) was a "textbook example" of an attempt to establish a synarchy, as it united politicians, the Catholic Church, and the Mafia-controlled drug economy.[11]
LaRouche Lyndon LaRouche, leader of a controversial movement on the political fringe,[12][13] describes a wide-ranging historical phenomenon, starting with Alexandre Saint-Yves d'Alveydre and the Martinist Order followed by important individuals, organizations, movements and regimes that are alleged to have been synarchist, including the government of Nazi Germany.[14] He claims that during the Great Depression an international coalition of financial institutions, raw materials cartels, and intelligence operatives, installed fascist regimes throughout Europe (and tried to do so in Mexico) to maintain world order and prevent the repudiation of international debts.[15] LaRouche identifies the former U.S. Vice President and former PNAC member Dick Cheney as a modern "synarchist", and claims that "synarchists" have "a scheme for replacing regular military forces of nations, by private armies in the footsteps of a privately financed international Waffen-SS-like scheme, a force deployed by leading financier institutions, such as the multi-billions funding by the U.S. Treasury, of Cheney's Halliburton gang."[16]
By
CNu
at
February 02, 2014
9
comments
![]()
Labels: Deep State , History's Mysteries
Saturday, February 01, 2014
The Meaning Of Dieudonné
By
CNu
at
February 01, 2014
15
comments
![]()
Labels: truth
Alexandre Saint-Yves Alveydre
By
CNu
at
February 01, 2014
0
comments
![]()
Labels: as above-so below , History's Mysteries , theoconservatism
Friday, January 31, 2014
SADM: special atomic demolition munitions
By
CNu
at
January 31, 2014
16
comments
![]()
Labels: Living Memory , tactical evolution , unspeakable
having served their purpose, disinfo operations finally get digested and excreted through the larouchian sphincter whale.to...,
By
CNu
at
January 31, 2014
1 comments
![]()
Labels: Ass Clownery , high strangeness , the wattles
but it had some strange twists and turns and was ongoing in the u.k. as well as the u.s...,
By
CNu
at
January 31, 2014
0
comments
![]()
Labels: History's Mysteries , Living Memory , unspeakable
not sure what they were working on that prompted them to renew the disinfo program from the 50's...,
By
CNu
at
January 31, 2014
0
comments
![]()
Labels: History's Mysteries , Living Memory , unspeakable
Thursday, January 30, 2014
stop listening to the rich and stupid
Because who better to solve the world’s problems than the people who benefit from the status quo?
By
CNu
at
January 30, 2014
21
comments
![]()
Labels: global system of 1% supremacy , you used to be the man
microbial market theory...,
By
CNu
at
January 30, 2014
0
comments
![]()
Labels: as above-so below , microcosmos
Wednesday, January 29, 2014
interwebs the greatest legal facilitator of inequality in human history?
By
CNu
at
January 29, 2014
12
comments
![]()
Labels: global system of 1% supremacy , Peak Capitalism
worsening inequality is the inevitable outcome of free market capitalism
By
CNu
at
January 29, 2014
0
comments
![]()
Labels: global system of 1% supremacy , Peak Capitalism
Tuesday, January 28, 2014
what drives success?
By
CNu
at
January 28, 2014
12
comments
![]()
Labels: cultural darwinism
the burglary that exposed the fbi's domestic surveillance and war on black folks...,
By
CNu
at
January 28, 2014
0
comments
![]()
Labels: American Original , History's Mysteries , Living Memory , People Centric Leadership , What IT DO Shawty...
paranoia of the plutocrats
By
CNu
at
January 28, 2014
0
comments
![]()
Labels: global system of 1% supremacy , you used to be the man
Monday, January 27, 2014
1% tryna play that Godwin's Law card...,
By
CNu
at
January 27, 2014
3
comments
![]()
Labels: global system of 1% supremacy , presstitution
bond villains pretending to be "good guys"...,
By
CNu
at
January 27, 2014
0
comments
![]()
Labels: global system of 1% supremacy , parasitic , Peak Capitalism
Chipocalypse Now - I Love The Smell Of Deportations In The Morning
sky | Donald Trump has signalled his intention to send troops to Chicago to ramp up the deportation of illegal immigrants - by posting a...

-
theatlantic | The Ku Klux Klan, Ronald Reagan, and, for most of its history, the NRA all worked to control guns. The Founding Fathers...
-
NYTimes | The United States attorney in Manhattan is merging the two units in his office that prosecute terrorism and international narcot...
-
Wired Magazine sez - Biologists on the Verge of Creating New Form of Life ; What most researchers agree on is that the very first functionin...