USPTO | United States Patent 7,572,449 Hill , et al. August 11, 2009
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Vaccine against Yersinia comprising one or two antibodies, one specific for Yersinia pestis F1-antigen and the other one for Yersinia pestis V-antigen
Abstract
The use of (i) an antibody specific for Yersinia pestis F1-antigen, or a binding fragment thereof, or (ii) an antibody specific for Yersinia pestis V-antigen, or a binding fragment thereof, or a combination of (i) and (ii), in the production of a medicament for the treatment of infection by Yersinia pestis. It has been found that such treatments are effective therapies for Yersinia pestis infection. In addition, the combination produces a synergistic effect when used prophylactically.
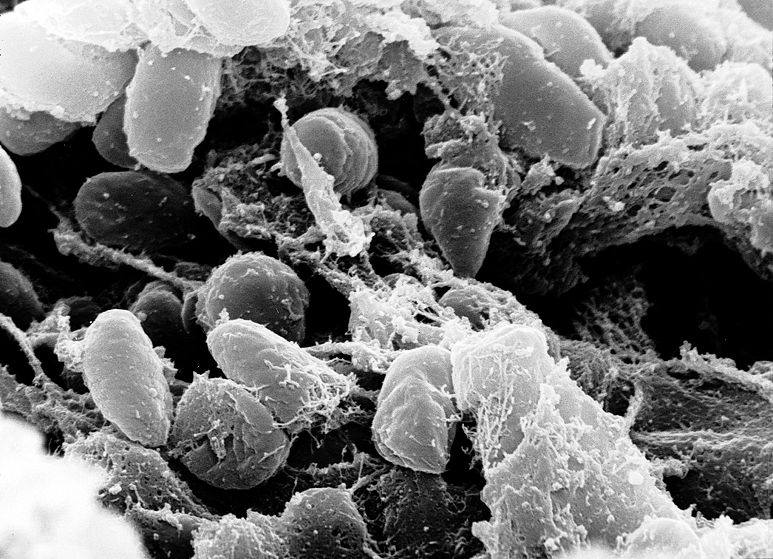
Yersinia pestis (formerly Pasteurella pestis) is a Gram-negative rod-shaped bacterium belonging to the family Enterobacteriaceae. It is a facultative anaerobe that can infect humans and other animals.
Human Y. pestis infection takes three main forms: pneumonic, septicemic, and the notorious bubonic plagues.[1] All three forms have been responsible for high mortality rates in epidemics throughout human history, including the Black Death (a bubonic plague) that accounted for the death of at least one-third of the European population in 1347 to 1353.
In September 2009 the death of a molecular genetics professor at the University of Chicago was linked to his work on a weakened strain of Y. pestis.[2].
Y. pestis has gained attention as a possible biological warfare agent and the CDC has classified it as a category A pathogen requiring preparation for a possible terrorist attack.


0 comments:
Post a Comment