howstuffworks | Unless you travel into the vacuum of space, sound is all around you every day. But most of the time, you probably don't think of it as a physical presence. You hear sounds; you don't touch them. The only exceptions may be loud nightclubs, cars with window-rattling speakers and ultrasound machines that pulverize kidney stones. But even then, you most likely don't think of what you feel as sound itself, but as the vibrations that sound creates in other objects.
The idea that something so intangible can lift objects can seem unbelievable, but it's a real phenomenon. Acoustic levitation takes advantage of the properties of sound to cause solids, liquids and heavy gases to float. The process can take place in normal or reduced gravity. In other words, sound can levitate objects on Earth or in gas-filled enclosures in space.
To understand how acoustic levitation works, you first need to know a little about gravity, air and sound. First, gravity is a force that causes objects to attract one another. The simplest way to understand gravity is through Isaac Newton's law of universal gravitation. This law states that every particle in the universe attracts every other particle. The more massive an object is, the more strongly it attracts other objects. The closer objects are, the more strongly they attract each other. An enormous object, like the Earth, easily attracts objects that are close to it, like apples hanging from trees. Scientists haven't decided exactly what causes this attraction, but they believe it exists everywhere in the universe.
Second, air is a fluid that behaves essentially the same way liquids do. Like liquids, air is made of microscopic particles that move in relation to one another. Air also moves like water does -- in fact, some aerodynamic tests take place underwater instead of in the air. The particles in gasses, like the ones that make up air, are simply farther apart and move faster than the particles in liquids.
Third, sound is a vibration that travels through a medium, like a gas, a liquid or a solid object. A sound's source is an object that moves or changes shape very rapidly. For example, if you strike a bell, the bell vibrates in the air. As one side of the bell moves out, it pushes the air molecules next to it, increasing the pressure in that region of the air. This area of higher pressure is a compression. As the side of the bell moves back in, it pulls the molecules apart, creating a lower-pressure region called a rarefaction. The bell then repeats the process, creating a repeating series of compressions and rarefactions. Each repetition is one wavelength of the sound wave.
The sound wave travels as the moving molecules push and pull the molecules around them. Each molecule moves the one next to it in turn. Without this movement of molecules, the sound could not travel, which is why there is no sound in a vacuum.
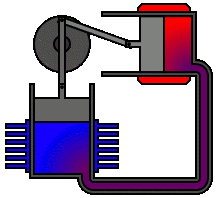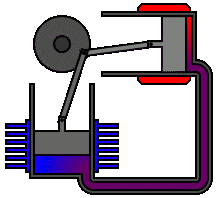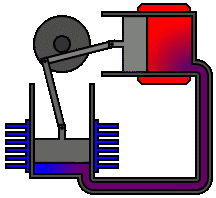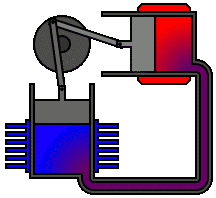
 The Physics of Sound Levitation
The Physics of Sound LevitationA basic acoustic levitator has two main parts -- a transducer, which is a vibrating surface that makes sound, and a reflector. Often, the transducer and reflector have concave surfaces to help focus the sound. A sound wave travels away from the transducer and bounces off the reflector. Three basic properties of this traveling, reflecting wave help it to suspend objects in midair.
First, the wave, like all sound, is a longitudinal pressure wave. In a longitudinal wave, movement of the points in the wave is parallel to the direction the wave travels. It's the kind of motion you'd see if you pushed and pulled one end of a stretched Slinky. Most illustrations, though, depict sound as a transverse wave, which is what you would see if you rapidly moved one end of the Slinky up and down. This is simply because transverse waves are easier to visualize than longitudinal waves.
Second, the wave can bounce off of surfaces. It follows the law of reflection, which states that the angle of incidence -- the angle at which something strikes a surface -- equals the angle of reflection -- the angle at which it leaves the surface. In other words, a sound wave bounces off a surface at the same angle at which it hits the surface. A sound wave that hits a surface head-on at a 90 degree angle will reflect straight back off at the same angle. The easiest way to understand wave reflection is to imagine a Slinky that is attached to a surface at one end. If you picked up the free end of the Slinky and moved it rapidly up and then down, a wave would travel the length of the spring. Once it reached the fixed end of the spring, it would reflect off of the surface and travel back toward you. The same thing happens if you push and pull one end of the spring, creating a longitudinal wave.
Finally, when a sound wave reflects off of a surface, the interaction between its compressions and rarefactions causes interference. Compressions that meet other compressions amplify one another, and compressions that meet rarefactions balance one another out. Sometimes, the reflection and interference can combine to create a standing wave. Standing waves appear to shift back and forth or vibrate in segments rather than travel from place to place. This illusion of stillness is what gives standing waves their name.
Standing sound waves have defined nodes, or areas of minimum pressure, and antinodes, or areas of maximum pressure. A standing wave's nodes are at the heart of acoustic levitation. Imagine a river with rocks and rapids. The water is calm in some parts of the river, and it is turbulent in others. Floating debris and foam collect in calm portions of the river. In order for a floating object to stay still in a fast-moving part of the river, it would need to be anchored or propelled against the flow of the water. This is essentially what an acoustic levitator does, using sound moving through a gas in place of water.
By placing a reflector the right distance away from a transducer, the acoustic levitator creates a standing wave. When the orientation of the wave is parallel to the pull of gravity, portions of the standing wave have a constant downward pressure and others have a constant upward pressure. The nodes have very little pressure.
In space, where there is little gravity, floating particles collect in the standing wave's nodes, which are calm and still. On Earth, objects collect just below the nodes, where the acoustic radiation pressure, or the amount of pressure that a sound wave can exert on a surface, balances the pull of gravity.
 TechnologyReview | Yet today, even with seemingly cost-effective cloud services available from the likes of Amazon, most companies still choose to operate their own computing resources—whether for corporate e-mail or financial trading—as if they were homeowners relying on generators for electricity. One reason they resist cloud computing, Casado says, is that network architecture is too decentralized to reconfigure easily, which leaves the cloud insecure and unreliable. Cloud computing providers tend to run entire data centers on one shared network. If, for example, Coke and Pepsi both entrusted their computer systems to one of today's public cloud services, they might share a network connection, even though their data stores would be carefully kept separate. That could pose a security risk: a hacker who accessed one company's data could see the other's. It would also mean that a busy day for Coke would cause Pepsi's data transfers to slow down.
TechnologyReview | Yet today, even with seemingly cost-effective cloud services available from the likes of Amazon, most companies still choose to operate their own computing resources—whether for corporate e-mail or financial trading—as if they were homeowners relying on generators for electricity. One reason they resist cloud computing, Casado says, is that network architecture is too decentralized to reconfigure easily, which leaves the cloud insecure and unreliable. Cloud computing providers tend to run entire data centers on one shared network. If, for example, Coke and Pepsi both entrusted their computer systems to one of today's public cloud services, they might share a network connection, even though their data stores would be carefully kept separate. That could pose a security risk: a hacker who accessed one company's data could see the other's. It would also mean that a busy day for Coke would cause Pepsi's data transfers to slow down.