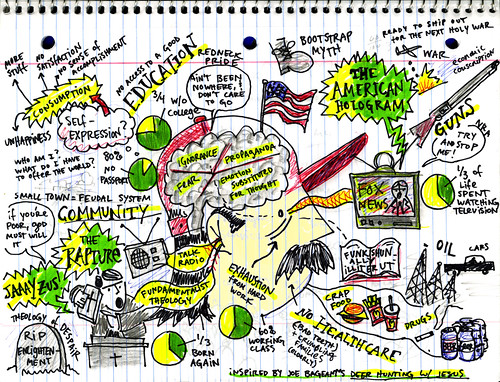
TruthDig | The political philosopher Sheldon Wolin uses the term “inverted totalitarianism” in his book “Democracy Incorporated” to describe our political system. It is a term that would make sense to Huxley. In inverted totalitarianism, the sophisticated technologies of corporate control, intimidation and mass manipulation, which far surpass those employed by previous totalitarian states, are effectively masked by the glitter, noise and abundance of a consumer society. Political participation and civil liberties are gradually surrendered. The corporation state, hiding behind the smokescreen of the public relations industry, the entertainment industry and the tawdry materialism of a consumer society, devours us from the inside out. It owes no allegiance to us or the nation. It feasts upon our carcass.
TruthDig | The political philosopher Sheldon Wolin uses the term “inverted totalitarianism” in his book “Democracy Incorporated” to describe our political system. It is a term that would make sense to Huxley. In inverted totalitarianism, the sophisticated technologies of corporate control, intimidation and mass manipulation, which far surpass those employed by previous totalitarian states, are effectively masked by the glitter, noise and abundance of a consumer society. Political participation and civil liberties are gradually surrendered. The corporation state, hiding behind the smokescreen of the public relations industry, the entertainment industry and the tawdry materialism of a consumer society, devours us from the inside out. It owes no allegiance to us or the nation. It feasts upon our carcass.The corporate state does not find its expression in a demagogue or charismatic leader. It is defined by the anonymity and facelessness of the corporation. Corporations, who hire attractive spokespeople like Barack Obama, control the uses of science, technology, education and mass communication. They control the messages in movies and television. And, as in “Brave New World,” they use these tools of communication to bolster tyranny. Our systems of mass communication, as Wolin writes, “block out, eliminate whatever might introduce qualification, ambiguity, or dialogue, anything that might weaken or complicate the holistic force of their creation, to its total impression.”
The result is a monochromatic system of information. Celebrity courtiers, masquerading as journalists, experts and specialists, identify our problems and patiently explain the parameters. All those who argue outside the imposed parameters are dismissed as irrelevant cranks, extremists or members of a radical left. Prescient social critics, from Ralph Nader to Noam Chomsky, are banished. Acceptable opinions have a range of A to B. The culture, under the tutelage of these corporate courtiers, becomes, as Huxley noted, a world of cheerful conformity, as well as an endless and finally fatal optimism. We busy ourselves buying products that promise to change our lives, make us more beautiful, confident or successful as we are steadily stripped of rights, money and influence. All messages we receive through these systems of communication, whether on the nightly news or talk shows like “Oprah,” promise a brighter, happier tomorrow. And this, as Wolin points out, is “the same ideology that invites corporate executives to exaggerate profits and conceal losses, but always with a sunny face.” We have been entranced, as Wolin writes, by “continuous technological advances” that “encourage elaborate fantasies of individual prowess, eternal youthfulness, beauty through surgery, actions measured in nanoseconds: a dream-laden culture of ever-expanding control and possibility, whose denizens are prone to fantasies because the vast majority have imagination but little scientific knowledge.”
Our manufacturing base has been dismantled. Speculators and swindlers have looted the U.S. Treasury and stolen billions from small shareholders who had set aside money for retirement or college. Civil liberties, including habeas corpus and protection from warrantless wiretapping, have been taken away. Basic services, including public education and health care, have been handed over to the corporations to exploit for profit. The few who raise voices of dissent, who refuse to engage in the corporate happy talk, are derided by the corporate establishment as freaks.
The façade is crumbling. And as more and more people realize that they have been used and robbed, we will move swiftly from Huxley’s “Brave New World” to Orwell’s “1984.” The public, at some point, will have to face some very unpleasant truths. The good-paying jobs are not coming back. The largest deficits in human history mean that we are trapped in a debt peonage system that will be used by the corporate state to eradicate the last vestiges of social protection for citizens, including Social Security. The state has devolved from a capitalist democracy to neo-feudalism. And when these truths become apparent, anger will replace the corporate-imposed cheerful conformity. The bleakness of our post-industrial pockets, where some 40 million Americans live in a state of poverty and tens of millions in a category called “near poverty,” coupled with the lack of credit to save families from foreclosures, bank repossessions and bankruptcy from medical bills, means that inverted totalitarianism will no longer work.